Your eyes are one of the most delicate and vital organs in your body. They allow you to see the world, connect with people, and enjoy life’s beauty. However, many people ignore early signs of eye problems, assuming they are temporary or unimportant. One such condition that requires immediate attention is Uveitis.
What is Uveitis?
Uveitis is a medical term used to describe inflammation of the uvea, the middle layer of the eye. The uvea consists of the iris (colored part of the eye), ciliary body, and choroid. These structures are responsible for blood supply to the eye and maintaining normal vision. When inflammation affects these areas, it can lead to significant discomfort and, if left untreated, even permanent vision loss.
Uveitis can affect people of any age and may occur in one or both eyes. The severity varies depending on the cause, but early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications.
Types of Uveitis
- Anterior Uveitis – Affects the front part of the eye (iris).
- Intermediate Uveitis – Involves the vitreous (gel-like fluid in the eye).
- Posterior Uveitis – Affects the retina and choroid.
- Panuveitis – Affects all parts of the uvea.
Among these, anterior uveitis is the most common and usually presents with pain, redness, and blurred vision.
What Causes Uveitis?
Uveitis can have multiple causes. Sometimes, it occurs due to autoimmune diseases, where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues. Common examples include rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and ankylosing spondylitis.
Infections are another cause. Conditions like tuberculosis (TB), herpes virus, syphilis, and toxoplasmosis can trigger inflammation in the eye. In some cases, eye injuries, surgeries, or even unknown factors (idiopathic) can lead to uveitis.
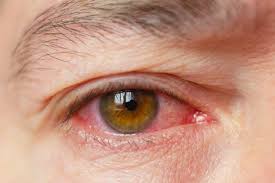
Symptoms of Uveitis
Recognizing the early symptoms of uveitis is crucial for protecting your vision. The most common signs include:
- Persistent eye redness
- Eye pain or soreness
- Blurred or cloudy vision
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Floaters (black spots in vision)
- Reduced or distorted vision
These symptoms can appear suddenly or develop gradually. Ignoring them may lead to serious eye damage.
Impact on Vision
If uveitis is not diagnosed and treated promptly, it can cause permanent damage to your eye structures. Some complications include:
- Cataract (clouding of the lens)
- Glaucoma (increased eye pressure causing nerve damage)
- Retinal detachment
- Optic nerve damage
- Permanent vision loss or blindness
Early treatment can prevent these severe outcomes.
Treatment of Uveitis
The goal of treatment is to reduce inflammation, relieve symptoms, and prevent vision loss. Treatment may include:
- Steroid eye drops to reduce inflammation
- Oral medications or injections for severe cases
- Immunosuppressant medicines if caused by autoimmune diseases
- Antibiotics or antivirals for infection-related uveitis
Regular monitoring by an ophthalmologist is crucial throughout the treatment.
Conclusion
Your eyesight is precious. If you experience any symptoms like eye redness, pain, or blurry vision, don’t ignore them. Consult an eye specialist immediately. Early detection and proper treatment of uveitis can protect your vision and ensure a healthier, brighter future.