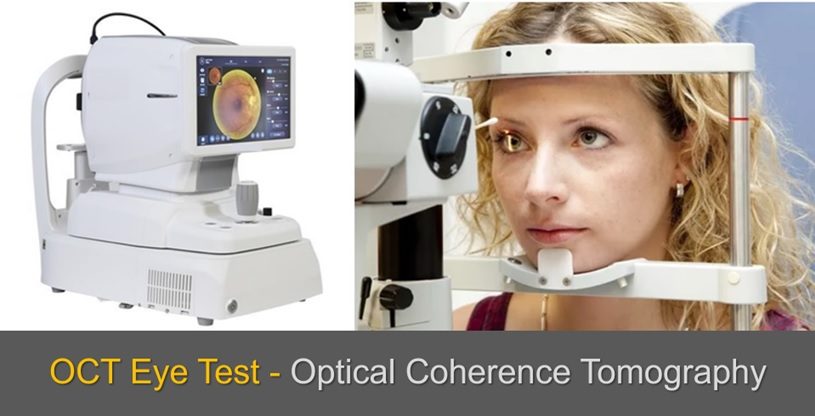
When it comes to eye health, early detection and precise diagnosis of issues are essential to prevent vision loss and maintain healthy eyesight. One of the most advanced technologies used in modern eye care is Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT). This non-invasive imaging test is commonly performed to diagnose various retinal and optic nerve conditions. But what exactly is an OCT eye test, and what should you expect during the procedure? In this detailed guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about the OCT test, from preparation to results, and why it’s an integral part of advanced eye care.
Understanding OCT Eye Test
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is an imaging technique that captures highly detailed cross-sectional images of the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye, as well as the optic nerve. It uses light waves to map out the layers of the retina and detect abnormalities that might not be visible through routine eye examinations. Think of it as an eye ultrasound, but instead of using sound waves, it employs light waves to create images of the retina’s structures.
The OCT test is used to diagnose and monitor conditions like:
- Glaucoma
- Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
- Diabetic Retinopathy
- Macular Edema
- Macular Hole
- Central Serous Retinopathy
- Retinal Detachment
- Vitreous Traction
It is also used to track the effectiveness of treatments, like injections for macular degeneration or laser surgery for diabetic retinopathy, by providing before-and-after images.
Why an OCT Test is Important
For many people, eye diseases like glaucoma or macular degeneration develop silently, showing no symptoms until significant damage has been done. OCT helps detect these conditions early by providing clear images of the retina’s different layers, allowing for timely intervention and treatment.
For patients already diagnosed with an eye condition, regular OCT tests help monitor disease progression and assess how well treatments are working. It’s a critical tool in preventing further vision loss.
Now that we understand the significance of OCT, let’s explore what to expect during the test.
Preparing for the OCT Eye Test
1. Scheduling the Test
The OCT eye test is typically recommended during routine eye exams for those at risk of retinal or optic nerve conditions. If your ophthalmologist has advised you to undergo an OCT test, you’ll be given an appointment to visit an eye clinic or hospital. The test is painless, quick, and does not require any special preparation, so you can go about your regular activities leading up to the test.
2. No Fasting or Medication Changes
Unlike some medical procedures, the OCT eye test doesn’t require fasting, nor do you need to adjust any medications you’re currently taking. If you wear glasses or contact lenses, you’ll likely be asked to remove them during the test, so it’s a good idea to bring your case for easy storage.
3. Dilation of the Pupils (Sometimes Required)
For some patients, the doctor may choose to dilate your pupils before the OCT test. This is done using special eye drops that widen the pupils, allowing for clearer images, especially when deeper layers of the retina need to be examined. Dilation is not always required for every patient, but it can be a necessary step depending on the condition being assessed.
If dilation is required, it’s important to note that your vision will be blurry for several hours following the test. Wearing sunglasses afterward will help reduce light sensitivity, and it’s recommended that you arrange for someone to drive you home if your pupils are dilated.
During the OCT Eye Test
1. Arriving at the Clinic
Once you arrive at the clinic, the test itself will be conducted in a specialized area with an OCT machine. This machine consists of a camera, light source, and computer system that captures and processes the retinal images. A technician or optometrist will guide you through the procedure and make sure you’re comfortable.
2. Seating and Positioning
You’ll be seated comfortably in front of the OCT machine, resting your chin on a chinrest and your forehead against a headrest. This setup ensures that your head remains stable during the scan, which is crucial for capturing clear and accurate images of your retina.
3. Focus on a Target Light
The test is painless and non-invasive. The technician will ask you to focus on a small light inside the machine. This light serves as a target for you to look at while the OCT device scans your eye. The machine then emits low-power light waves that bounce off your retina to create high-resolution images of its layers. No contact is made with your eye, and there’s no discomfort from the machine.
4. The Scanning Process
Once you’re properly positioned and focused, the scanning process begins. You’ll be asked to keep your eyes still, but don’t worry if you blink— the machine will still be able to capture the necessary images. In some cases, you may be asked to blink before the scan to ensure your eyes remain moist and prevent any dryness from affecting the results.
The scan takes just a few seconds per eye, and multiple images will be taken to provide a comprehensive view of the retina. If both eyes are being tested, the process is repeated for the second eye.
5. No Discomfort or Recovery Time
One of the greatest benefits of the OCT test is that it’s completely painless and non-invasive. There’s no contact with the eye, no bright flashes of light, and no physical discomfort during or after the test. Once the images are captured, you’re free to leave the machine. The entire process, from setup to completion, usually takes no more than 10 to 15 minutes.
After the OCT Eye Test
1. Results and Analysis
After the OCT test, the images are immediately available for analysis by your ophthalmologist or retina specialist. These images show cross-sectional views of the retina, highlighting its different layers and any abnormalities that may be present. The doctor will carefully examine these images for signs of diseases like macular degeneration, glaucoma, or diabetic retinopathy, and compare them with previous scans if applicable.
2. Discussion with Your Doctor
Following the test, your doctor will sit down with you to discuss the results. If any conditions are detected, they will explain what the images show and what treatment options are available. If you’re undergoing the test to monitor a previously diagnosed condition, the doctor will compare the new images with past results to assess the progression of the disease.
3. Next Steps
Based on the findings of the OCT test, your doctor will recommend the next steps. If an eye condition is detected, you may be prescribed medication, referred for further tests, or scheduled for regular follow-up OCT scans to monitor your condition. In some cases, surgical or laser treatments may be necessary, depending on the severity of the issue.
For patients who are using OCT to track the effectiveness of ongoing treatments (such as injections for macular degeneration), the results will help guide future treatment decisions and adjustments.
Benefits of the OCT Eye Test
1. Early Detection of Eye Diseases
OCT is a powerful tool for detecting eye diseases in their early stages, often before any symptoms appear. Conditions like glaucoma and macular degeneration can be managed more effectively when caught early, helping to preserve vision and prevent irreversible damage.
2. Non-Invasive and Painless
The OCT test is entirely non-invasive, meaning there’s no discomfort or need for recovery time. Patients can undergo the procedure without anxiety, and there are no side effects or risks involved.
3. Highly Accurate Imaging
OCT provides incredibly detailed images of the retina, allowing doctors to see even the smallest abnormalities that could indicate a developing condition. This accuracy helps in making precise diagnoses and tailoring treatment plans to each patient’s specific needs.
4. Monitoring Disease Progression
For patients already diagnosed with a retinal condition, OCT is an essential tool for monitoring disease progression. Regular scans help doctors assess whether a treatment is working and make necessary adjustments to the patient’s care plan.
Final Thoughts
The OCT eye test is one of the most advanced tools in ophthalmology today. Whether you’re at risk for a retinal disease, managing an ongoing eye condition, or simply undergoing a routine check-up, this quick and painless test provides invaluable insight into your eye health. By offering highly detailed images of the retina, OCT enables early detection, accurate diagnoses, and effective treatment plans that can preserve vision and improve quality of life.
If you’ve been recommended for an OCT eye test, you can expect a smooth, efficient process with no discomfort, allowing you to quickly return to your normal activities. At Chetna Hospital, we are committed to providing the latest in eye care technology, ensuring that our patients receive the best possible care.
For Consultation Contact us on 9168690448
Website – www.chetnahospital.co.in
Address – Chetna Hospital, Sambhajinagar, MIDC, G Block, Near Rotary Club, Chinchwad 411019
.
.
.
#hospital#pune#pcmc#chinchwad#medical#medicalservices#dryeyetreatment#dryeyerelief#dryeyedisease#dryeyetherapy#catract#catractsurgery#catracteyesurgery#catracteyeoperation#eyedoctor#eye#glaucoma#conjunctivitis#ophthalmologist#eyediseases#eyepain#pinkeye#hazeleyes#myopia#eyeinfection#amblyopia#dryeyesyndrome#eyeproblems#motibindu#motibinduoperation