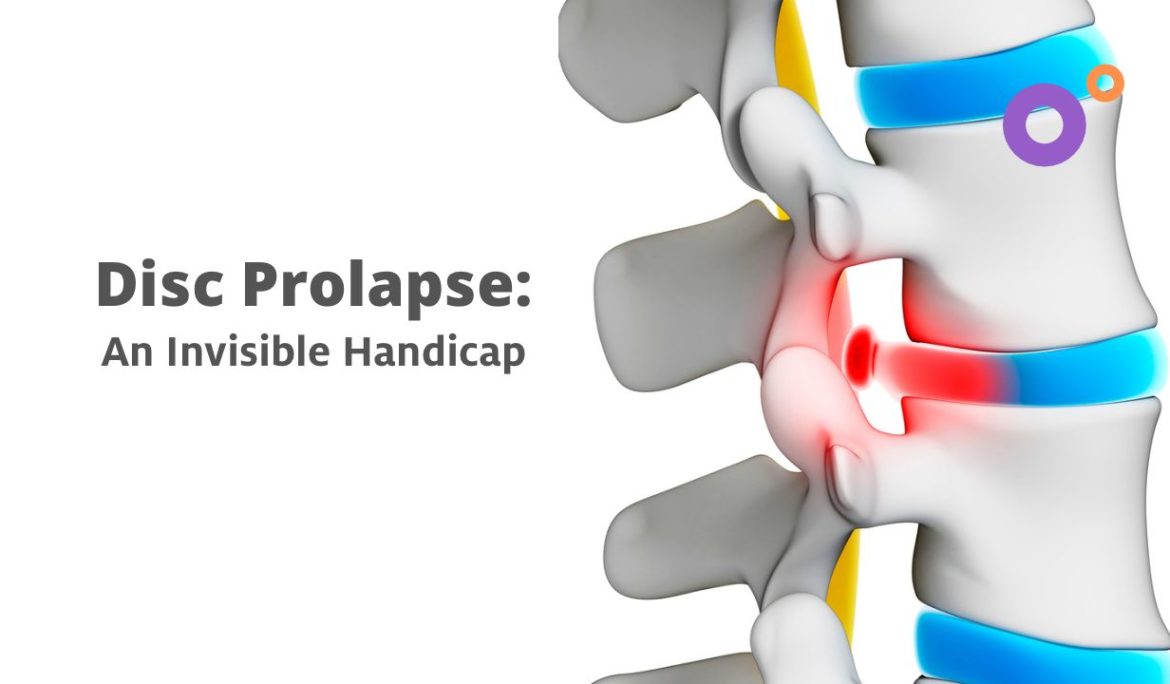
Prolapsed disc herniation, commonly known as a herniated disc, is a condition that affects the spinal discs, which act as cushions between the vertebrae. When a disc herniates, the inner gel-like material protrudes through a tear in the outer layer, potentially compressing nearby nerves and leading to pain, numbness, or weakness.
Causes
Several factors can contribute to a prolapsed disc herniation:
- Age-Related Degeneration: As we age, spinal discs lose hydration and elasticity, making them more susceptible to injury.
- Repetitive Strain: Jobs or activities that involve heavy lifting, twisting, or prolonged sitting can increase the risk of a herniated disc.
- Injury: Sudden trauma, such as an accident or fall, can lead to disc herniation.
- Genetics: A family history of disc problems may increase susceptibility to herniation.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a herniated disc can vary based on the location of the herniation and the nerves affected. Common signs include:
- Localized Pain: Pain may be felt in the lower back or neck, depending on the location of the herniation.
- Radiating Pain: Nerve compression can cause pain that radiates down the legs (sciatica) or arms.
- Numbness and Tingling: Affected nerves may lead to sensations of numbness or tingling in the extremities.
- Muscle Weakness: In severe cases, weakness in the muscles supplied by the affected nerve can occur, impacting mobility.
Diagnosis
A healthcare provider will typically conduct a physical examination and may recommend imaging tests, such as MRI or CT scans, to confirm a diagnosis of prolapsed disc herniation. These tests help visualize the extent of the herniation and identify any nerve compression.
Treatment Options
Treatment for a herniated disc often begins conservatively:
- Physical Therapy: Exercises can strengthen back muscles and improve flexibility, alleviating pressure on the disc.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications can help manage pain and inflammation.
- Epidural Injections: Corticosteroid injections may be administered to reduce inflammation around the affected nerve.
In cases where conservative treatment fails, surgical options may be considered:
- Discectomy: Removal of the herniated portion of the disc to relieve nerve compression.
- Laminectomy: Removal of a small section of bone over the nerve root to provide additional space.
- Spinal Fusion: In some cases, fusing two vertebrae may be necessary to stabilize the spine.
Conclusion
Prolapsed disc herniation can significantly impact quality of life, but with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, many individuals experience relief from symptoms and regain normal function. If you suspect you have a herniated disc, consult a healthcare professional to discuss your symptoms and explore the best treatment options for you. Taking proactive steps toward spinal health can help prevent future issues and maintain overall well-being.
For Consultation Contact us on 9158680739
Website – www.chetnahospital.co.in
Address – Chetna Hospital, Sambhajinagar, MIDC, G Block, Near Rotary Club, Chinchwad 411019…#pune#pcmc#chinchwad#hospital#medical#medicalservices#spinesurgeon#backspecialist#sciatica#sciaticnerve#sciaticapain#sciaticatreatment#spinesurgery#spinespecialist#spinedoctor#backpaindoctor#endoscopicspinesurgery#orthopaedicsurgeon#mistlifsurgery#cervicalpain#spinalcord#rediculopathy#backpainrelief#slippeddisc#spine#neckpain#spinalstenosis#lumberlordosis#backbonesurgery