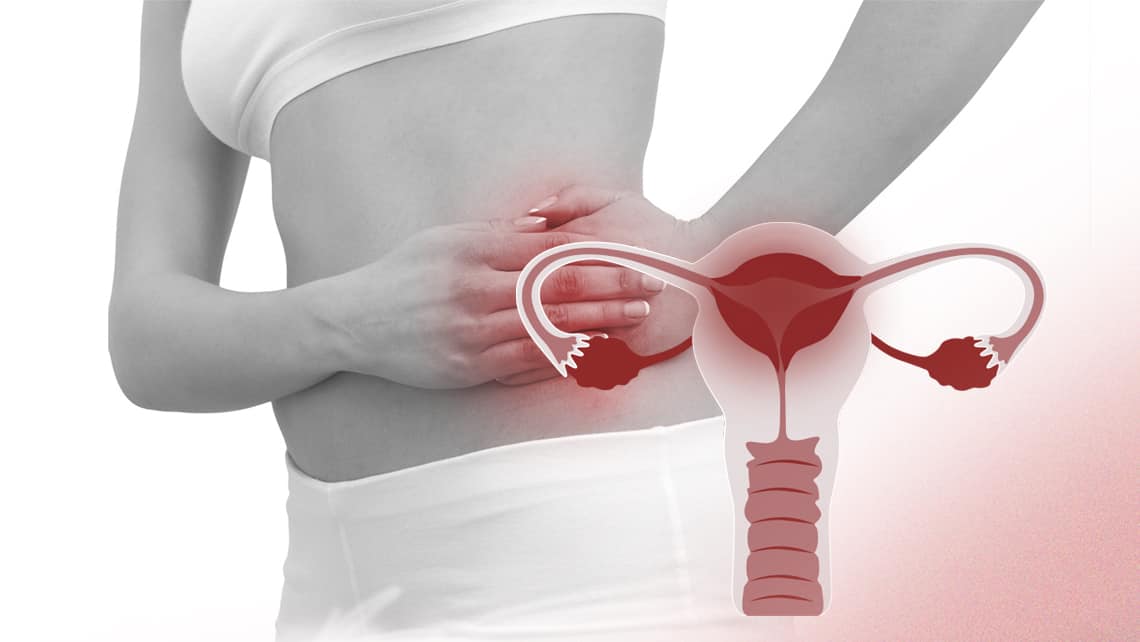
Introduction: Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) is a common yet serious infection of the female reproductive organs. It can lead to severe complications such as infertility, chronic pelvic pain, and ectopic pregnancy if left untreated. This comprehensive guide aims to provide in-depth insights into PID, covering its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
- What is Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)? Pelvic Inflammatory Disease refers to the inflammation and infection of the female reproductive organs, including the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. It typically occurs when sexually transmitted bacteria, most commonly chlamydia and gonorrhea, spread from the vagina and cervix to the upper reproductive tract.
- Causes of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease: The primary cause of PID is bacterial infection, often resulting from sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as chlamydia and gonorrhea. Other bacteria, including those found in the vagina’s normal flora, can also contribute to PID development. Risk factors for PID include multiple sexual partners, a history of STIs, and inconsistent condom use.
- Symptoms of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease: PID symptoms can vary in severity and may include pelvic pain, abnormal vaginal discharge, irregular menstrual bleeding, painful urination, fever, and pain during intercourse. However, PID can also be asymptomatic, making early detection challenging. Any unusual symptoms in the pelvic area should prompt medical evaluation.
- Diagnosis of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease: Diagnosing PID involves a combination of medical history assessment, pelvic examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Doctors may perform tests to detect STIs, such as nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) or cultures. Pelvic ultrasound and laparoscopy may be used to visualize the reproductive organs and assess for inflammation or other abnormalities.
- Complications of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease: Untreated PID can lead to serious complications, including chronic pelvic pain, infertility, ectopic pregnancy, and an increased risk of pelvic adhesions and ovarian abscesses. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent these long-term consequences.
- Treatment Options for Pelvic Inflammatory Disease: The primary goal of PID treatment is to eradicate the causative bacteria and reduce inflammation. Antibiotics are typically prescribed to target the identified pathogens. In severe cases or when complications arise, hospitalization and intravenous antibiotics may be necessary. Sexual partners should also be treated to prevent reinfection.
- Prevention Strategies for Pelvic Inflammatory Disease: Preventing PID involves practicing safe sex, including consistent condom use and limiting sexual partners. Routine screening for STIs, especially in high-risk individuals, can aid in early detection and treatment. Prompt treatment of STIs can help prevent the progression to PID. Additionally, vaccination against certain STIs, such as human papillomavirus (HPV), can reduce PID risk.
- Conclusion: Pelvic Inflammatory Disease poses significant health risks to women of reproductive age. Understanding its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies is essential for promoting early detection, prompt intervention, and optimal outcomes. By raising awareness and adopting preventive measures, individuals can take proactive steps to safeguard their reproductive health and well-being.
In conclusion, Pelvic Inflammatory Disease is a complex condition with potentially severe consequences if left untreated. Through education, proactive screening, and the promotion of safe sexual practices, the burden of PID can be reduced, leading to improved reproductive health outcomes for women worldwide.
#hospital #pune #pcmc #chinchwad#health #healthcare #gynaecologist #femalegynaecologist #gynaecologistappointment #gynac #gynaecologistdoctor #gynaecologisthospital #goodgynaecologist #gynaecologistspecialist