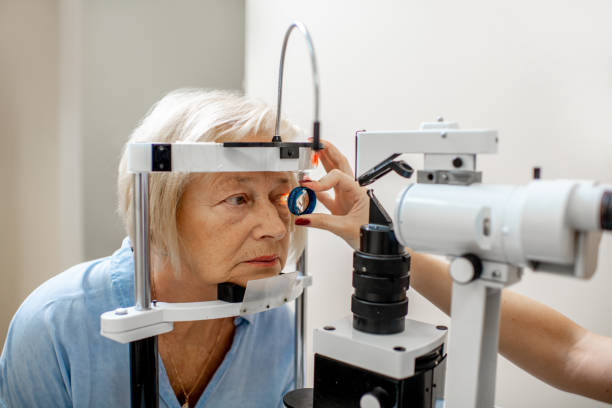
What is Perimetry?
Perimetry, also known as visual field testing, is a diagnostic method used to evaluate a person’s field of vision. This test measures the entire area that can be seen when the eyes are focused on a central point. It helps detect blind spots, also known as scotomas, which can be indicative of various eye conditions, including glaucoma.
When is a Perimetry Test Done?
A perimetry test is typically performed when a patient experiences symptoms such as vision loss, visual field disturbances, or when there is a need to monitor the progression of eye diseases. It is a crucial tool in the early detection and management of glaucoma, a condition that can lead to irreversible vision loss if not properly treated.
How Long Does It Take to Assess Your Visual Field?
The duration of a perimetry test can vary, but it generally takes about 20 to 30 minutes per eye. During the test, the patient is asked to look at a central point and respond to visual stimuli presented in their peripheral vision. The results are then analyzed to determine the extent of the visual field.
The Crucial Role of Perimetry Testing in Diagnosing Glaucoma
Perimetry testing plays a vital role in diagnosing glaucoma. Glaucoma often affects peripheral vision first, which can go unnoticed by the patient in the early stages. By identifying these peripheral vision changes, perimetry tests can detect glaucoma before significant damage occurs. Regular visual field testing allows for timely intervention and management, helping to preserve vision and prevent further deterioration.
Beyond Glaucoma: Other Diseases Identified through Perimetry Testing
While perimetry is essential for diagnosing and monitoring glaucoma, it can also help identify other eye conditions. These include:
- Retinal diseases such as retinitis pigmentosa and age-related macular degeneration
- Optic nerve damage from conditions like optic neuritis or brain tumors
- Neurological conditions affecting the visual pathways
How Often Should You Perform This Test?
The frequency of perimetry testing depends on individual risk factors and the presence of eye conditions. For patients diagnosed with glaucoma, the test is typically performed once or twice a year to monitor disease progression. Those with high risk factors for glaucoma, such as a family history or elevated intraocular pressure, may also require regular testing. Your eye care professional will recommend the appropriate testing interval based on your specific needs.
Why is the Visual Field Test So Important for Glaucoma?
The visual field test is crucial for glaucoma management because it helps detect changes in vision that are not always apparent to the patient. Glaucoma can progress slowly, and vision loss may go unnoticed until the condition is advanced. Regular visual field tests allow for the early detection of changes, enabling timely treatment to slow or halt disease progression and preserve vision.
Who Needs to Check Their Visual Fields?
Visual field testing is recommended for:
- Individuals over the age of 40, especially those with a family history of glaucoma
- Patients diagnosed with glaucoma or other eye diseases affecting the visual field
- Individuals experiencing unexplained vision loss or visual disturbances
- Those with conditions that can affect the optic nerve or brain
Uses of Visual Field Test
The visual field test has several important uses, including:
- Diagnosing glaucoma and other eye conditions
- Monitoring the progression of eye diseases
- Assessing the effectiveness of treatments for glaucoma and other visual disorders
- Identifying visual field defects caused by neurological conditions
In summary, perimetry testing is a vital tool in the early detection, diagnosis, and management of glaucoma and other visual disorders. Regular testing helps preserve vision and improve the quality of life for patients. If you are at risk for glaucoma or experiencing vision changes, consult your eye care professional about scheduling a perimetry test.