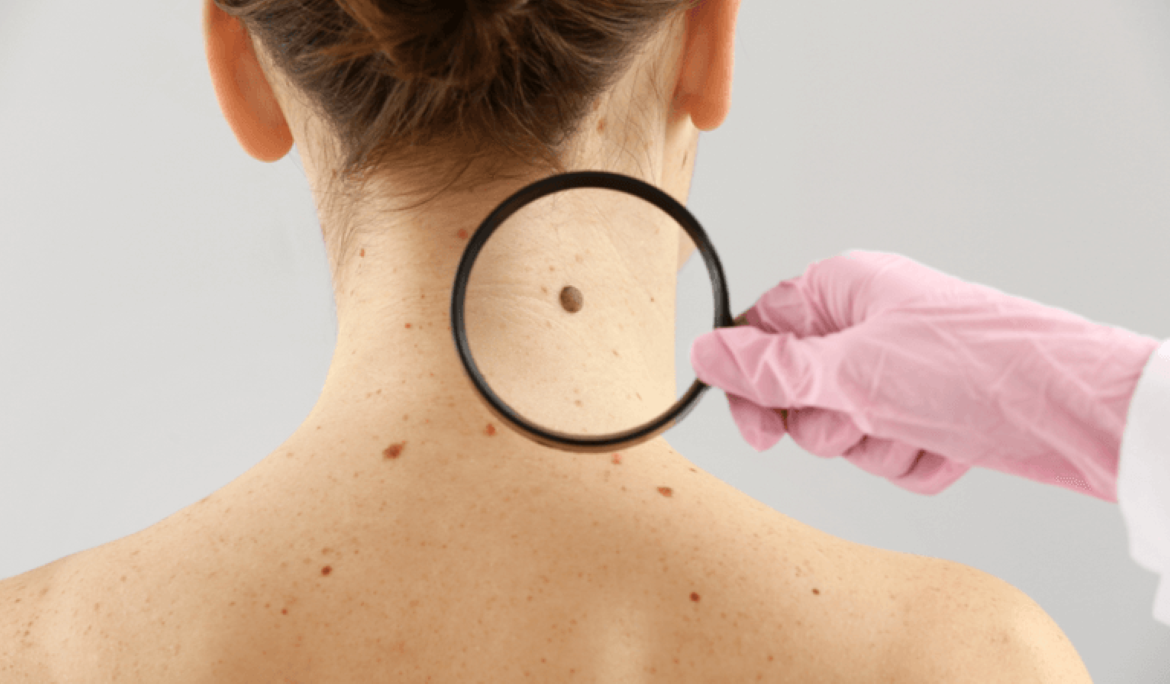
Moles are common skin growths that can appear anywhere on the body. While most moles are harmless, some people choose to have them removed for cosmetic reasons or because of discomfort. In other cases, mole removal becomes necessary when there are signs of changes that may indicate a potential skin condition. Thanks to advancements in dermatology, mole removal is now safe, precise, and scar-minimizing.
Two of the most trusted and effective methods for mole removal are Radiofrequency (RF) Ablation and Surgical Excision. In this blog, we’ll explore what these methods involve, who can benefit from them, and how to choose the right treatment for your skin.
What Is a Mole?
A mole, or melanocytic nevus, is a collection of pigmented cells that often appear as small brown, black, or skin-colored spots. Moles can be flat or raised and vary in size and shape. They usually develop in childhood or adolescence and may change slowly over time. While most moles are benign (non-cancerous), some can become atypical or cancerous, requiring medical evaluation.
Why Do People Remove Moles?
There are several reasons why someone may choose to remove a mole:
- Cosmetic Concerns: Many people feel self-conscious about moles, especially if they are on the face, neck, or other visible areas.
- Physical Discomfort: Raised moles on friction areas (like the collar line or underarms) can rub against clothing and cause irritation.
- Medical Reasons: Moles that change in color, size, or shape—or start to bleed or itch—may need to be removed and sent for biopsy to rule out malignancy.
- Preventive Care: Sometimes, dermatologists recommend removing a mole if there’s a risk of it turning into a cancerous lesion in the future.
Mole Removal Methods: An Overview
There are various techniques to remove moles, but Radiofrequency Ablation and Surgical Excision are two of the most widely used and dermatologist-recommended methods.
1. Radiofrequency (RF) Mole Removal
Radiofrequency ablation is a non-invasive or minimally invasive technique that uses high-frequency electrical energy to cut and coagulate the targeted tissue. In simple terms, it “melts away” the mole using controlled radio waves.
✅ Benefits of RF Mole Removal:
- Quick procedure (often takes just 10–15 minutes)
- Minimal or no bleeding
- No stitches required
- Little to no scarring
- Fast healing
- Suitable for small, raised, and benign moles
💡 Ideal Candidates:
- Patients with small, superficial moles
- Individuals looking for cosmetic mole removal
- People concerned about scarring from traditional surgery
⚠️ Aftercare:
- Keep the area clean and dry for a few days
- Apply prescribed ointments as directed
- Avoid sun exposure on the treated area
- Follow-up visit may be required depending on healing
2. Surgical Excision
Surgical excision involves cutting out the mole entirely with a scalpel, including a small margin of surrounding skin. It is typically done under local anesthesia and may require stitches.
✅ Benefits of Surgical Excision:
- Complete removal of deeper or larger moles
- Allows the mole to be sent for biopsy
- Low chance of recurrence if removed correctly
- Ideal for irregular or suspicious moles
💡 Ideal Candidates:
- Patients with large, deep, or flat moles
- Anyone whose mole has changed in color, size, or shape
- Individuals with moles in high-friction or injury-prone areas
⚠️ Aftercare:
- Keep the stitches dry for 24–48 hours
- Avoid strenuous activities until stitches are removed
- Watch for signs of infection (redness, pus, swelling)
- Follow up with your dermatologist for stitch removal and healing check
![]() For Consultation: 96077 53535 / 9158681123
For Consultation: 96077 53535 / 9158681123
![]() Website: www.chetnahospital.co.in
Website: www.chetnahospital.co.in
![]() Address: Chetna Hospital, Sambhajinagar, MIDC, G Block, Near Rotary Club, Chinchwad 411019
Address: Chetna Hospital, Sambhajinagar, MIDC, G Block, Near Rotary Club, Chinchwad 411019
.
.
.
#hospital#pune#pcmc#chinchwad#health#healthcare#skin#dermatologist#skinspecialist#skinclinic#hairdermatologist#skindoctor#dermatologistappointment#skincareprofessional#derma#skindr