Introduction
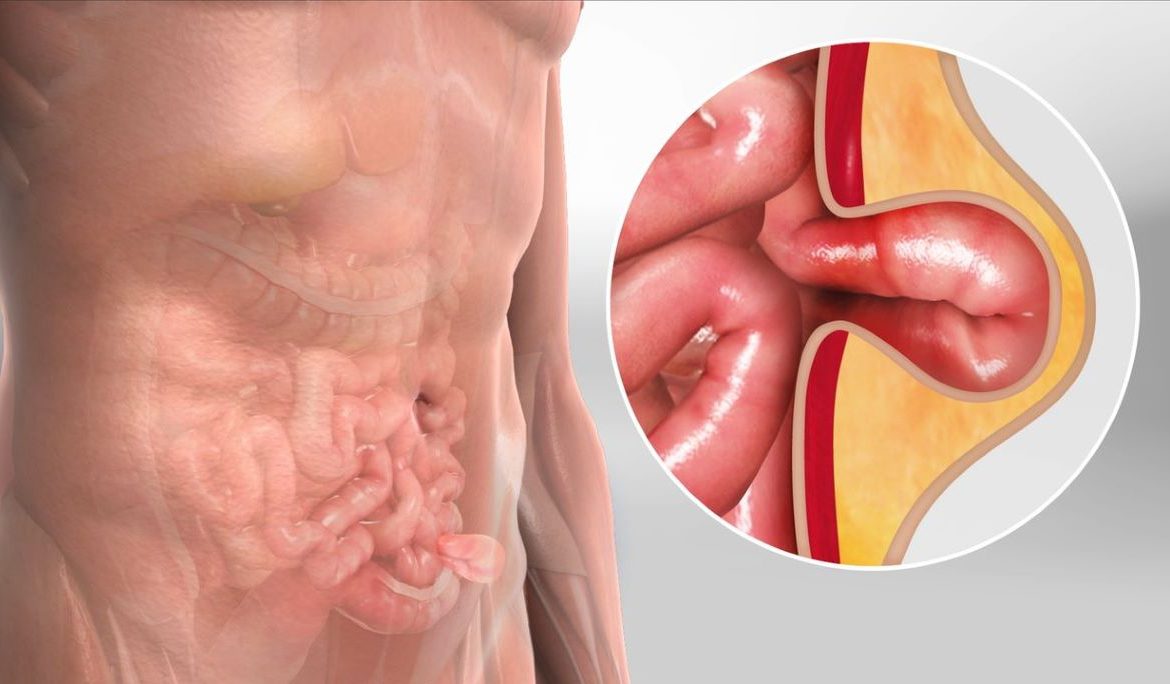
A hernia is a common medical condition that occurs when an organ or fatty tissue pushes through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. While hernias can develop in different parts of the body, they most commonly affect the abdominal and groin regions. Though not all hernias are life-threatening, they can cause discomfort, pain, and complications if left untreated.
This blog will discuss the causes, symptoms, types, diagnosis, and treatment options for hernias, helping you understand when to seek medical attention and the importance of timely treatment.
What Causes a Hernia?
Hernias are primarily caused by a combination of muscle weakness and strain. Several factors can contribute to their development, including:
✅ Congenital Defects – Some people are born with weak muscles, making them more prone to hernias. ✅ Heavy Lifting – Lifting heavy objects without proper technique can strain abdominal muscles. ✅ Chronic Coughing or Sneezing – Persistent cough due to smoking, lung disease, or allergies can weaken muscles. ✅ Straining During Bowel Movements – Chronic constipation can put excessive pressure on the abdomen. ✅ Obesity – Excess weight increases pressure on the abdominal wall. ✅ Pregnancy – Expanding uterus stretches and weakens abdominal muscles. ✅ Aging – Natural muscle weakening over time can contribute to hernia development. ✅ Previous Surgery – Incisional hernias can develop at the site of a surgical incision.
Common Symptoms of a Hernia
The symptoms of a hernia vary depending on its type and severity. However, common signs include:
🔹 Visible Bulge – A lump or swelling that may become more noticeable when standing, lifting, or coughing. 🔹 Pain or Discomfort – A dull aching sensation, especially after physical activity. 🔹 Heaviness or Pressure – A dragging sensation in the abdomen or groin. 🔹 Burning or Aching Feeling – Near the affected area. 🔹 Weakness in the Affected Muscle Area – Difficulty performing certain activities. 🔹 Acid Reflux or Difficulty Swallowing – Common in hiatal hernia cases. 🔹 Nausea and Vomiting – If the hernia is strangulated, it can become a medical emergency. 🔹 Bulge That Doesn’t Go Back In – A strangulated hernia can cut off blood flow, requiring urgent medical attention.
Types of Hernias
Hernias can occur in different parts of the body. The most common types include:
1. Inguinal Hernia (Groin Hernia)
🔹 Most common type of hernia, occurring more frequently in men. 🔹 Happens when part of the intestine or fatty tissue pushes into the groin area. 🔹 May cause pain, swelling, and discomfort, especially while bending or lifting.
2. Umbilical Hernia
🔹 Occurs when part of the intestine pushes through the abdominal wall near the belly button. 🔹 Common in infants and pregnant women. 🔹 Typically painless but may require surgery if it persists.
3. Femoral Hernia
🔹 More common in women, particularly after pregnancy. 🔹 Develops in the upper thigh or groin area. 🔹 Higher risk of complications if left untreated.
4. Hiatal Hernia
🔹 Happens when the stomach pushes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity. 🔹 Common symptoms include acid reflux, heartburn, and difficulty swallowing. 🔹 Can often be managed with lifestyle changes but may require surgery in severe cases.
5. Incisional Hernia
🔹 Occurs at the site of a previous surgical incision. 🔹 Common in people who have had abdominal surgeries. 🔹 May enlarge over time and require surgical repair.
6. Epigastric Hernia
🔹 Develops in the upper abdomen, between the belly button and chest. 🔹 Usually small but can cause discomfort or pain.
7. Spigelian Hernia
🔹 Occurs along the edge of the rectus abdominis muscle. 🔹 Less common but can be difficult to diagnose.
Diagnosis of a Hernia
A hernia diagnosis is typically made through:
✅ Physical Examination – A doctor checks for a bulge, especially when coughing or straining. ✅ Ultrasound – Helps detect hidden hernias. ✅ CT Scan or MRI – Used for complex or internal hernias. ✅ Endoscopy (for Hiatal Hernias) – Examines the esophagus and stomach.
Treatment Options for Hernia
The treatment for a hernia depends on its size, severity, and symptoms. The primary options include:
1. Watchful Waiting
✔️ If the hernia is small and not causing pain, doctors may recommend monitoring it over time. ✔️ Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding heavy lifting may help prevent worsening.
2. Hernia Belt or Truss
✔️ Provides temporary relief by holding the hernia in place. ✔️ Not a permanent solution and should only be used under medical supervision.
3. Surgery
If the hernia is large, painful, or at risk of complications, surgery is the best treatment. The two main surgical approaches are:
🔹 Open Surgery – A single large incision is made, and the hernia is repaired using sutures or a mesh. 🔹 Laparoscopic Surgery – A minimally invasive procedure using small incisions and a camera to repair the hernia with a mesh.
✅ Laparoscopic surgery has a shorter recovery time and minimal scarring, making it the preferred option for many patients.
Post-Surgery Care & Recovery
After hernia surgery, following proper care instructions ensures a smooth recovery:
✔️ Avoid Heavy Lifting – No strenuous activities for at least 4-6 weeks. ✔️ Follow a Healthy Diet – Prevent constipation to reduce strain. ✔️ Stay Active – Light walking helps prevent complications. ✔️ Take Prescribed Medications – For pain relief and infection prevention. ✔️ Watch for Complications – Report fever, severe pain, or unusual swelling to your doctor immediately.
Preventing Hernias
Although some hernias are unavoidable, you can take steps to reduce the risk:
✅ Maintain a healthy weight. ✅ Avoid heavy lifting or use proper techniques. ✅ Treat chronic coughing or sneezing. ✅ Stay hydrated and eat fiber-rich foods to prevent constipation. ✅ Strengthen abdominal muscles with regular exercise.
When to See a Doctor?
Seek medical attention if you experience: 🔹 Persistent pain or discomfort. 🔹 A growing bulge that doesn’t go away. 🔹 Nausea, vomiting, or difficulty passing stool. 🔹 A sudden increase in pain, which could indicate strangulation.
Conclusion
A hernia is a common yet manageable condition. While some small hernias can be monitored, surgery is the only permanent solution for larger or symptomatic cases. If you notice symptoms, consult a qualified surgeon for proper diagnosis and treatment. Early intervention ensures a smoother recovery and prevents complications.
If you’re experiencing symptoms of a hernia, book a consultation today! 🩺