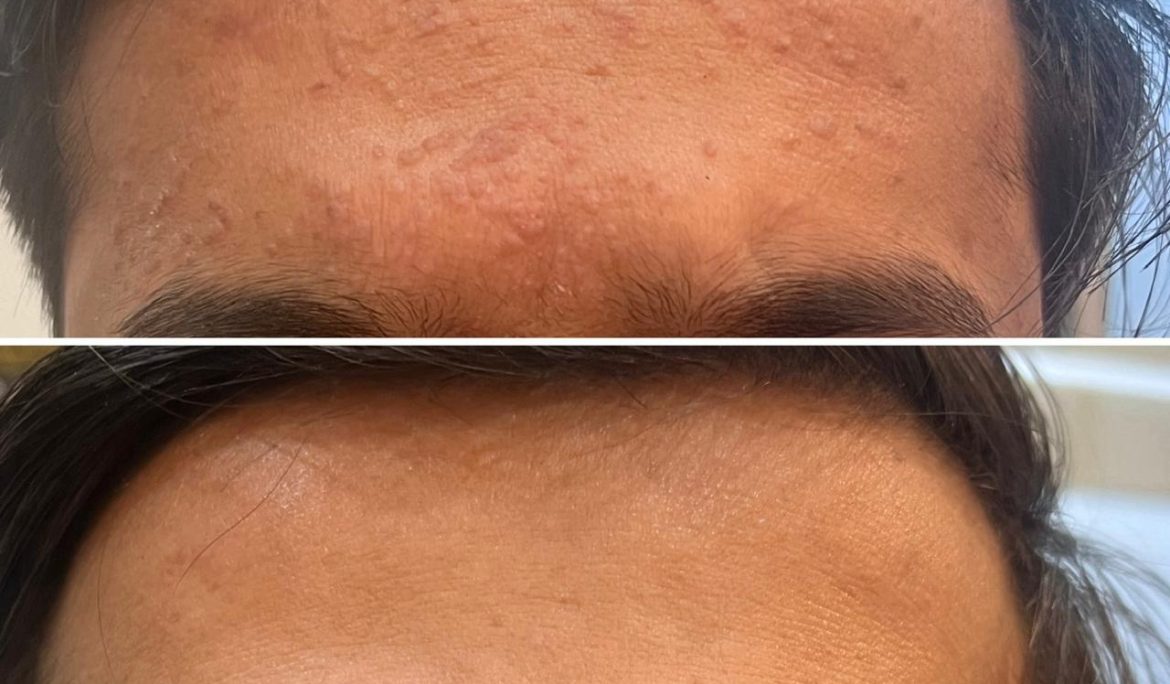
Introduction – Warts are a common dermatological condition caused by viral infections. Despite being generally harmless, warts can be unsightly and sometimes uncomfortable. In this extensive guide, we’ll delve into the various aspects of warts, including their causes, types, prevention strategies, and available treatment options.
- Understanding Warts – Warts are small, non-cancerous growths on the skin caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV infects the top layer of the skin, leading to rapid cell growth and the formation of a wart. Warts can appear anywhere on the body, including the hands, feet, face, and genital area. They are highly contagious and can spread through direct contact with an infected person or contaminated surfaces.
- Types of Warts – There are several types of warts, each with distinct characteristics:
- Common Warts: Typically found on the hands, fingers, and around the nails, common warts are rough, raised, and often have a cauliflower-like appearance.
- Plantar Warts: These warts develop on the soles of the feet, causing pain or discomfort when walking due to pressure on the wart.
- Flat Warts: Flat warts are small, smooth, and flat-topped lesions that can appear in clusters on the face, arms, or legs.
- Genital Warts: Genital warts are sexually transmitted and appear in the genital and anal areas. They are caused by specific strains of HPV and require medical attention.
- Filiform Warts: Filiform warts are long and narrow, often found on the face, neck, or eyelids. They have a distinctive appearance and can be easily irritated.
- Causes of Warts – Warts are caused by HPV, a group of viruses with more than 100 different strains. However, not all HPV strains cause warts, and some are associated with more severe health conditions such as cervical cancer. The transmission of HPV occurs through direct skin-to-skin contact or contact with contaminated surfaces, such as shared towels or surfaces in public spaces like swimming pools or locker rooms. Certain factors can increase the risk of developing warts, including a weakened immune system, skin injuries or cuts, and frequent exposure to HPV.
- Symptoms of Warts – The symptoms of warts can vary depending on the type and location of the wart. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Raised, rough, or smooth skin growths
- Clusters of warts in a localized area
- Pain or tenderness, especially with plantar warts
- Itching or irritation
- Changes in skin texture or color around the wart
- Diagnosis of Warts – Diagnosing warts is usually straightforward and can often be done through a visual examination by a healthcare professional, such as a dermatologist. In some cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis, especially if the wart appears unusual or if there are concerns about other skin conditions.
- Prevention of Warts – While it may not be possible to completely eliminate the risk of warts, certain preventive measures can reduce the likelihood of infection:
- Practice good hand hygiene, including regular handwashing with soap and water.
- Avoid touching warts on yourself or others to prevent spreading the virus.
- Keep skin cuts or abrasions clean and covered to reduce the risk of HPV entry.
- Use protective footwear in public places like swimming pools or locker rooms to avoid exposure to HPV on contaminated surfaces.
- Limit close contact with individuals who have visible warts, especially during intimate activities.
#hospital #pune #pcmc #chinchwad #health #healthcare #skin #dermatologist #skinspecialist #skinclinic #hairdermatologist #skindoctor #dermatologistappointment #skincareprofessional #derma #skindr #pimples #acne #warts #wartsremoval