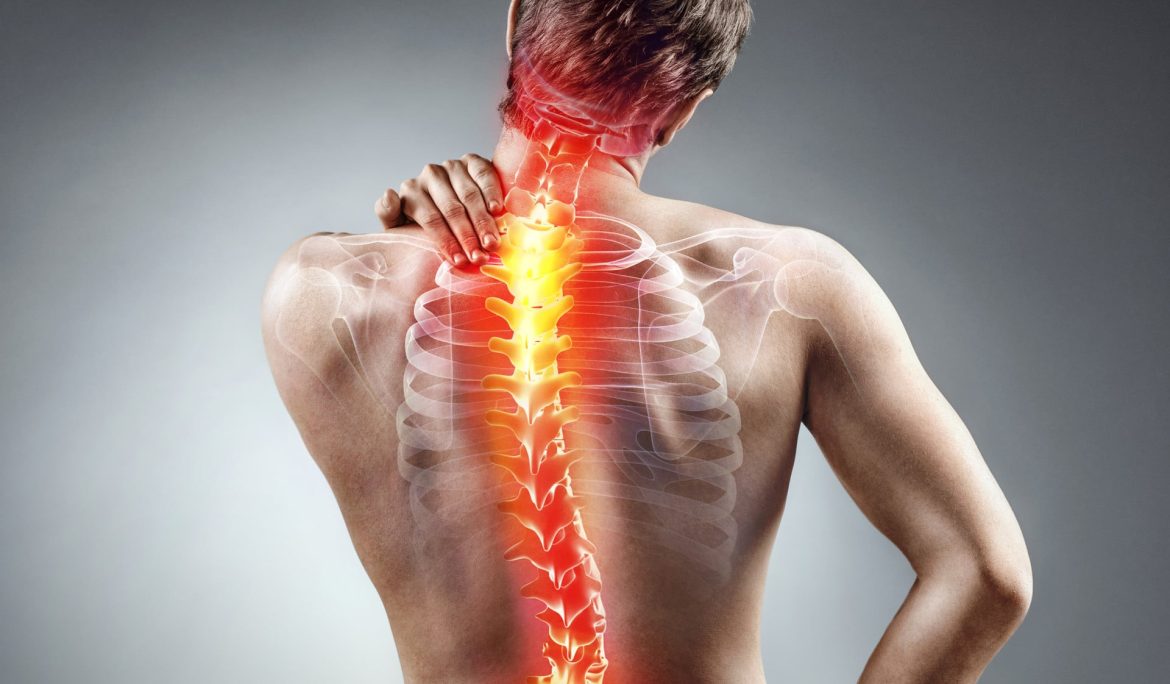
Back pain is one of the most common health problems affecting people of all ages. Whether it’s a dull ache after a long day at work or a sharp pain that makes it hard to move, back pain can significantly affect your quality of life. While some causes are minor and resolve with rest, others may be a sign of a serious spine condition that requires medical attention.
In this article, we’ll explore the most common causes of back pain and guide you on when it’s time to see a spine specialist.
Why Back Pain Happens
Your spine is a complex structure made up of bones (vertebrae), discs, ligaments, muscles, and nerves. It supports your body’s weight, allows flexibility, and protects your spinal cord. Because of this complexity, there are many possible reasons for back pain — from muscle strain to nerve compression.
Common Causes of Back Pain
1. Slipped Disc (Herniated Disc)
Between each vertebra in your spine is a soft, jelly-like cushion called a disc. Its job is to absorb shock and allow smooth movement. Sometimes, due to injury or wear and tear, the disc can slip out of place or rupture, pressing on nearby nerves.
Symptoms include:
- Pain radiating to the arms or legs
- Numbness or tingling in the limbs
- Pain that worsens with movement
Common triggers: Heavy lifting, sudden twisting, or trauma.
2. Poor Posture
Slouching over your computer, hunching your shoulders, or sitting in one position for too long can strain the muscles and ligaments in your back. Over time, poor posture can lead to chronic pain and even structural changes in the spine.
Tips to improve posture:
- Keep your screen at eye level
- Sit with your feet flat on the floor
- Take breaks to stand and stretch every hour
3. Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis occurs when the spinal canal narrows, putting pressure on the spinal cord and nerves. This condition is often age-related but can also occur due to injury or arthritis.
Symptoms include:
- Back or neck pain
- Weakness or numbness in arms or legs
- Difficulty walking or maintaining balance
4. Degenerative Disc Disease
As we age, the discs between our vertebrae can lose water and flexibility. This natural aging process reduces their cushioning ability, causing stiffness and pain.
Common signs:
- Pain that comes and goes
- Pain that worsens with sitting or bending
- Relief when lying down
5. Muscle or Ligament Strain
Lifting heavy objects improperly, sudden movements, or even vigorous exercise can strain the muscles or ligaments in your back.
Symptoms:
- Sudden, sharp pain
- Muscle spasms
- Stiffness and reduced mobility
6. Osteoporosis
In osteoporosis, bones become brittle and weak, increasing the risk of fractures in the spine. Even small falls or simple movements can cause compression fractures, leading to sudden and severe back pain.
7. Other Causes
While the above are common, back pain can also result from:
- Arthritis
- Scoliosis (curvature of the spine)
- Infections in the spine
- Tumors (rare but serious)
When to See a Spine Specialist
While mild back pain often improves with rest, stretching, and over-the-counter pain relief, some symptoms signal the need for professional evaluation.
You should see a spine specialist if you have:
- Persistent Pain – Back or neck pain lasting more than 2–3 weeks despite rest and home care.
- Radiating Pain – Pain traveling down your arms or legs, often linked to nerve compression.
- Weakness or Numbness – Loss of strength, tingling, or numbness in the limbs.
- Severe Pain After Injury – Pain following a fall, accident, or sports injury.
- Loss of Bladder or Bowel Control – This is a medical emergency that could indicate nerve damage (Cauda Equina Syndrome).
- Difficulty Moving – Trouble bending, turning, or walking without pain.
- Spinal Deformity – Visible changes in your back’s shape or alignment.
Why Early Consultation Matters:
A spine specialist can diagnose the underlying cause of your pain using advanced imaging techniques and suggest the most effective treatment — which may be non-surgical in many cases. Early treatment often means faster recovery and reduced risk of long-term complications.
Treatment Options for Back Pain
The right treatment depends on the cause and severity of your condition. Common approaches include:
- Medications – Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and muscle relaxants.
- Physiotherapy – Exercises to strengthen muscles, improve posture, and restore mobility.
- Lifestyle Modifications – Ergonomic adjustments, weight management, and posture correction.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures – Such as injections for pain relief.
- Surgery – Only recommended when conservative methods fail or if there’s severe nerve compression.
Preventing Back Pain
While not all back pain is preventable, you can reduce your risk by:
- Maintaining good posture
- Staying active with regular exercise
- Avoiding heavy lifting (or lifting correctly)
- Using ergonomic furniture
- Maintaining a healthy weight
Final Thoughts
Back pain may be common, but it should never be ignored — especially if it’s persistent, severe, or affecting your daily activities. Recognizing the warning signs early and consulting a spine specialist can make a world of difference in your recovery and overall spine health.
Remember: Your spine supports your entire body — take care of it, and it will take care of you.
For Consultation Contact us on 9158680739 / 9158681123
Website - www.chetnahospital.co.in
Address – Chetna Hospital, Sambhajinagar, MIDC, G Block, Near Rotary Club, Chinchwad 411019
.
.
.
#pune#pcmc#chinchwad#hospital#medical#medicalservices#spinesurgeon#backspecialist#sciatica#sciaticnerve#sciaticapain#sciaticatreatment#spinesurgery#spinespecialist#spinedoctor#backpaindoctor#endoscopicspinesurgery#orthopaedicsurgeon#mistlifsurgery#cervicalpain#spinalcord#rediculopathy#backpainrelief#slippeddisc#spine#neckpain#spinalstenosis#lumberlordosis#backbonesurgery