Cervical cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting women worldwide. It occurs in the cervix, the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. Although it is a serious health condition, the good news is that cervical cancer is both preventable and treatable if detected in the early stages. With proper awareness, screening, and preventive measures such as vaccination, thousands of lives can be saved every year.
In this blog, we will explore the causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of cervical cancer in detail.
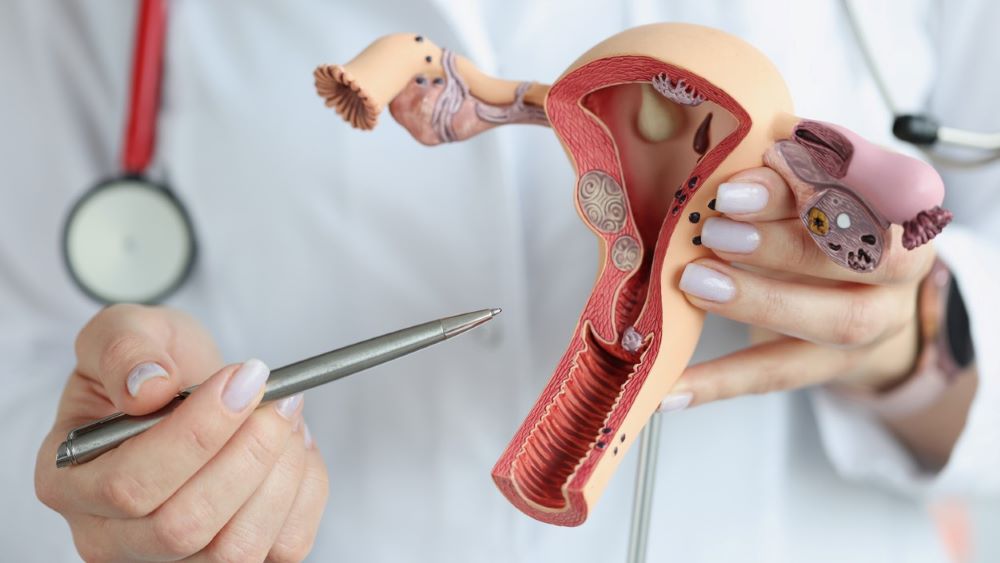
What is Cervical Cancer?
The cervix is a vital part of the female reproductive system. Cervical cancer begins when abnormal cells in the lining of the cervix grow uncontrollably and form a tumor. Over time, if left untreated, these abnormal cells can spread deeper into the cervix and surrounding tissues, eventually spreading to other parts of the body (a process known as metastasis).
Cervical cancer typically develops slowly, starting with precancerous changes called cervical dysplasia. These changes can be detected early with routine screening tests like the Pap smear or HPV test.
Causes of Cervical Cancer
The primary cause of cervical cancer is persistent infection with certain strains of the Human Papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is a very common sexually transmitted infection, and in most cases, the body clears the virus naturally. However, when the infection persists, it can cause abnormal changes in cervical cells, which may develop into cancer over time.
Other contributing causes and factors include:
- Early sexual activity – increases the risk of HPV infection.
- Multiple sexual partners – higher exposure to HPV.
- Smoking – chemicals in cigarettes make cervical cells more vulnerable to cancer.
- Weakened immune system – due to conditions like HIV or prolonged illness.
- Long-term use of oral contraceptives – slightly increases risk.
- Poor hygiene and lack of awareness – leading to delayed diagnosis.
Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
In its early stages, cervical cancer often shows no symptoms, which makes regular screening extremely important. As the disease progresses, women may experience the following signs:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding (after intercourse, between periods, or after menopause).
- Unusual vaginal discharge with foul smell.
- Pelvic pain or backache.
- Pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse.
- Fatigue, loss of appetite, and weight loss in advanced stages.
These symptoms are not always due to cancer, but they should never be ignored. Timely consultation with a gynecologist is crucial.
Screening and Diagnosis
Early detection of cervical cancer saves lives. The following tests are commonly used:
- Pap Smear Test – A simple and painless procedure where cells from the cervix are collected and examined for abnormalities.
- HPV Test – Detects high-risk strains of HPV that are most likely to cause cervical cancer.
- Colposcopy – A special magnifying device used to closely examine the cervix if Pap smear results are abnormal.
- Biopsy – Removal of a small tissue sample from the cervix for laboratory testing.
Doctors may also recommend imaging tests such as CT scans, MRIs, or PET scans to determine the stage of the cancer.
Prevention of Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is one of the most preventable cancers. Women can significantly reduce their risk by following these preventive measures:
1. HPV Vaccination
- The HPV vaccine protects against the most dangerous strains of the virus.
- It is most effective when given between ages 9 to 14, but women up to 45 years can also benefit.
- Both boys and girls should receive the vaccine to reduce the spread of HPV.
2. Regular Screening
- Pap smear tests should begin at the age of 21 and be repeated every 3 years.
- Women aged 30–65 should have a Pap smear plus HPV test every 5 years.
- Regular check-ups help detect precancerous changes before they turn into cancer.
3. Lifestyle Modifications
- Quit smoking to reduce the risk of cervical and other cancers.
- Practice safe sex by using protection and limiting the number of sexual partners.
- Maintain good personal hygiene.
- Boost immunity through a healthy diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep.
Treatment of Cervical Cancer
The treatment plan depends on the stage of cancer, the patient’s age, and overall health. Common treatment options include:
- Surgery – Removal of cancerous tissues or the entire uterus (hysterectomy) if required.
- Radiation Therapy – High-energy rays used to destroy cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy – Use of strong medicines to kill or stop the growth of cancer cells.
- Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy – Advanced treatments to specifically target cancer cells and boost the immune system.
With early detection, treatment outcomes are very positive. In advanced cases, treatment focuses on controlling cancer, relieving symptoms, and improving quality of life.
Living with and Beyond Cervical Cancer
A cervical cancer diagnosis can be emotionally challenging, but with proper support, women can continue to lead fulfilling lives. Support groups, counseling, and family encouragement play a vital role in the healing journey.
Regular follow-up care after treatment is essential to monitor for recurrence and manage side effects. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, eating nutritious food, and staying physically active further improves recovery.
Key Takeaways
- Cervical cancer is caused mainly by persistent HPV infection.
- Early stages usually have no symptoms – regular screening is vital.
- Prevention is possible with HPV vaccination, safe lifestyle choices, and timely Pap smears.
- Early diagnosis ensures successful treatment and saves lives.
Conclusion
Cervical cancer remains a major health concern for women, especially in countries where awareness and screening are limited. However, it is a cancer that we can prevent, control, and cure with the right measures. By spreading awareness, encouraging regular health check-ups, and ensuring access to HPV vaccination, we can move towards a future where no woman loses her life to cervical cancer.
At Chetna Hospital, our expert gynecologists and oncologists are dedicated to providing comprehensive screening, prevention, and treatment for cervical cancer. Remember—early detection is the key. Take charge of your health today and protect yourself and your loved ones.
For Consultation Contact us on 9168690447 / 9158681123
Website –
Address – Chetna Hospital, Sambhajinagar, MIDC, G Block, Near Rotary Club, Chinchwad 411019
.
.
.
#hospital#pune#pcmc#chinchwad#health#healthcare#gynaecologist#femalegynaecologist#gynaecologistappointment#gynac#gynaecologistdoctor#gynaecologisthospital#goodgynaecologist#gynaecologistspecialist.