Bleeding while passing stool is a concerning symptom that many people choose to ignore, attributing it to minor issues like constipation or temporary irritation. However, this symptom could be an indicator of underlying health conditions requiring medical intervention, sometimes even surgery. In this blog, we’ll discuss the possible causes of rectal bleeding, when to seek professional help, and the treatment options available.
Understanding Rectal Bleeding
Rectal bleeding refers to blood seen in or around the stool, on toilet paper, or in the toilet bowl after a bowel movement. The color of the blood can vary—bright red blood usually indicates a lower gastrointestinal (GI) issue, while dark or tar-like stools may suggest a problem higher up in the digestive tract.
Although it can be harmless in some cases, recurring or severe bleeding should not be ignored, as it might signify serious medical conditions such as colorectal cancer or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Common Causes of Bleeding While Passing Stool
Several conditions can cause bleeding during bowel movements. Identifying the cause is essential for effective treatment.
- Piles (Hemorrhoids):
- Swollen and inflamed veins in the rectum or anus.
- Symptoms: Bright red bleeding, itching, and discomfort during bowel movements.
- Risk Factors: Chronic constipation, prolonged sitting, and pregnancy.
- Anal Fissures:
- Small tears in the anal lining, often caused by passing hard stools.
- Symptoms: Sharp pain and a small amount of blood on the toilet paper.
- Fistulas or Abscesses:
- Infection around the anal area leading to pus-filled pockets or abnormal passages.
- Symptoms: Persistent pain, swelling, and blood-streaked stools.
- Colorectal Polyps or Cancer:
- Growths in the colon or rectum that may bleed as they grow.
- Symptoms: Changes in bowel habits, persistent bleeding, and weight loss.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD):
- Chronic inflammation of the digestive tract, including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
- Symptoms: Diarrhea, abdominal pain, and blood or mucus in stool.
- Diverticulosis or Diverticulitis:
- Small bulging pouches in the colon wall that may become inflamed or infected.
- Symptoms: Sudden bleeding and abdominal pain.
- Rectal Ulcers or Proctitis:
- Inflammation of the rectum, often due to infections or radiation therapy.
- Symptoms: Pain, bleeding, and an urgent need to defecate.
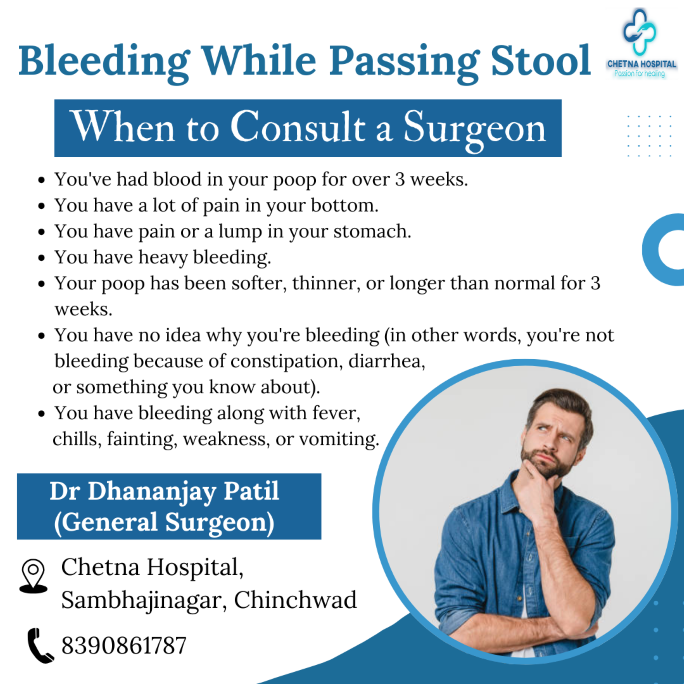
When to Consult a Surgeon
While occasional bleeding from minor issues like constipation may not be alarming, certain signs require immediate attention.
Red Flags to Watch For:
- Persistent Bleeding: If bleeding lasts for more than a few days or recurs frequently.
- Blood Mixed with Stool: Indicates internal bleeding, potentially from the colon.
- Dark, Tarry Stools: Suggests bleeding from the upper digestive tract.
- Severe Pain or Swelling: Points to conditions like abscesses or fistulas.
- Accompanying Symptoms: Fever, fatigue, anemia, or unexplained weight loss.
Ignoring these symptoms can lead to complications such as infections, anemia, or progression of serious conditions like colorectal cancer.
The Diagnostic Process
When you consult a surgeon for rectal bleeding, they will begin by gathering a detailed medical history and performing a physical examination. Further diagnostics may include:
- Digital Rectal Examination (DRE):
- A quick examination to check for abnormalities in the rectum.
- Colonoscopy:
- A procedure where a camera examines the entire colon to detect polyps, ulcers, or tumors.
- Sigmoidoscopy:
- Focuses on the rectum and lower part of the colon for localized issues.
- Proctoscopy:
- Used to examine the rectum and anal canal in detail.
- Blood Tests:
- To check for anemia or signs of infection.
These tests help pinpoint the exact cause and severity of the condition, enabling the surgeon to plan appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options for Rectal Bleeding
Treatment varies based on the cause, severity, and overall health of the patient. Options range from lifestyle modifications to surgical interventions.
1. Lifestyle and Non-Surgical Treatments:
- Dietary Changes: High-fiber foods and increased water intake to ease bowel movements.
- Medications: Stool softeners, anti-inflammatory drugs, or creams for piles and fissures.
- Sitz Baths: Warm water baths to soothe the anal area.
2. Minimally Invasive Procedures:
- Laser Surgery: Commonly used for piles and fissures, offering quicker recovery.
- Band Ligation: A rubber band technique to treat hemorrhoids.
- Sclerotherapy: Injection of chemicals to shrink hemorrhoids.
3. Surgical Interventions:
- Hemorrhoidectomy: Removal of severe hemorrhoids.
- Fistula Repair: Surgical correction of abnormal anal passages.
- Polyp or Tumor Removal: In cases of colorectal cancer, part of the colon may need removal.
Surgeons prioritize minimally invasive procedures whenever possible to ensure faster recovery and minimal discomfort.
Post-Treatment Care and Prevention
To prevent recurrence and aid recovery, consider the following tips:
- Maintain a High-Fiber Diet: Include fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to prevent constipation.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water daily.
- Regular Exercise: Helps improve bowel movements and overall health.
- Avoid Straining: Don’t delay bathroom visits, and avoid excessive force during bowel movements.
- Follow-Up Care: Regular check-ups with your doctor or surgeon are crucial, especially after a procedure.
Why Early Consultation Matters
Delaying a visit to the doctor for rectal bleeding can lead to complications. Early intervention ensures:
- Timely diagnosis and treatment.
- Prevention of complications like infections, severe anemia, or advanced cancer.
- Improved quality of life with quicker recovery.
Surgeons are equipped with advanced tools and expertise to address the root cause of rectal bleeding effectively.
Conclusion
Bleeding while passing stool is not something to ignore. It could stem from benign conditions like piles or indicate more serious issues like colorectal cancer. Knowing the symptoms and consulting a surgeon promptly can save lives.
If you or someone you know is experiencing rectal bleeding, don’t delay. Seek expert advice to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment. Prioritize your health today—it’s always better to act early than regret later.
For Consultation Contact us on 8390861787
Website – www.chetnahospital.co.in
Address – Chetna Hospital, Sambhajinagar, MIDC, G Block, Near Rotary Club, Chinchwad 411019
.
.
.
#pune#pcmc#chinchwad#hospital#medical#medicalservices#health#healthcare#surgery#generalsurgery#medicalprocedure#generalsurgeon#generalsurgeoninchinchwad