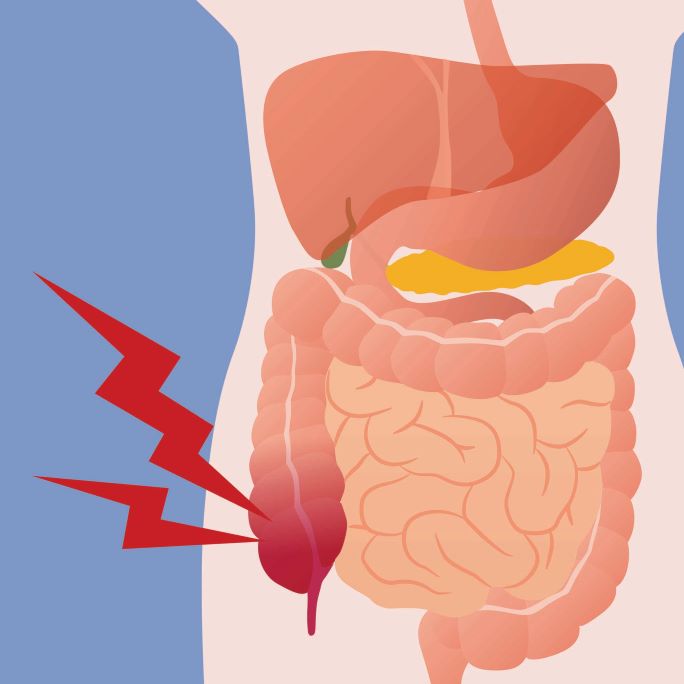
Appendicitis is a medical condition that occurs when the appendix, a small finger-shaped organ attached to the large intestine, becomes inflamed. It is one of the most common causes of emergency abdominal surgery. If left untreated, an inflamed appendix can rupture, leading to serious complications. This blog will cover everything you need to know about appendicitis, including its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
What is Appendicitis?
The appendix is a small pouch located in the lower right side of the abdomen. While its exact function remains unclear, it is believed to play a minor role in the immune system. Appendicitis occurs when the appendix becomes inflamed due to a blockage, infection, or other underlying causes.
Appendicitis is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention. A ruptured appendix can spread infection throughout the abdomen, causing a life-threatening condition known as peritonitis.
Causes of Appendicitis
The exact cause of appendicitis is not always clear, but several factors can contribute to its development:
- Blockage in the Appendix – A blockage due to hardened stool, foreign objects, or an enlarged lymph node can obstruct the opening of the appendix, leading to inflammation.
- Bacterial Infection – Infections in the digestive tract can cause swelling and irritation in the appendix.
- Gastrointestinal Infections – Viruses or bacteria affecting the gastrointestinal tract can lead to appendicitis.
- Trauma or Injury – Abdominal injuries may contribute to inflammation of the appendix.
- Tumors or Growths – In rare cases, tumors in the appendix can obstruct its opening and cause appendicitis.
Symptoms of Appendicitis
Appendicitis symptoms typically develop quickly, often within 24 to 48 hours. Common symptoms include:
- Abdominal Pain – The most common symptom, usually starting near the belly button and shifting to the lower right abdomen.
- Loss of Appetite – A sudden lack of interest in food can be an early sign.
- Nausea and Vomiting – Often occurs after the onset of abdominal pain.
- Fever and Chills – A mild fever may accompany the pain, indicating an infection.
- Bloating and Gas – Some patients experience abdominal swelling and excessive gas.
- Constipation or Diarrhea – Changes in bowel movements may occur.
- Pain Worsening with Movement – Activities such as walking, coughing, or pressing on the lower right abdomen can intensify the pain.
If you or someone you know experiences these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately to prevent complications.
Diagnosing Appendicitis
A doctor will use a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests to confirm appendicitis:
1. Physical Examination
- The doctor checks for tenderness in the lower right abdomen.
- A “rebound tenderness” test may be performed, where pressing the abdomen and quickly releasing it causes sharp pain.
2. Blood Tests
- A high white blood cell count indicates an infection.
3. Urine Test
- Helps rule out urinary tract infections or kidney stones.
4. Imaging Tests
- Ultrasound – A non-invasive test that can detect an inflamed appendix.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography) – Provides detailed images of the appendix to confirm inflammation.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) – Often used for pregnant women to avoid radiation exposure.
Treatment for Appendicitis
Appendicitis requires prompt medical intervention. The treatment options include:
1. Surgical Removal of the Appendix (Appendectomy)
Appendectomy is the most common and effective treatment for appendicitis. There are two types of appendectomy:
- Laparoscopic Appendectomy – A minimally invasive procedure involving small incisions and a camera-guided surgical approach. It results in quicker recovery and less pain.
- Open Appendectomy – Involves a larger incision in the lower abdomen and is performed when the appendix has ruptured or when complications arise.
2. Antibiotic Treatment
In some cases, mild appendicitis may be treated with antibiotics alone. However, surgery is usually recommended to prevent recurrence.
3. Drainage of Abscess (If Appendix Has Ruptured)
If the appendix has burst and formed an abscess, doctors may drain the pus before performing surgery.
Recovery After Appendectomy
After surgery, patients usually recover within a few weeks. Here are some post-surgery care tips:
- Rest and Avoid Strenuous Activities – Give your body time to heal.
- Stay Hydrated and Eat a Healthy Diet – Soft foods and fiber-rich meals aid digestion.
- Pain Management – Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribed medication can help reduce discomfort.
- Monitor for Signs of Infection – Look for redness, swelling, or discharge from the surgical site.
- Gradual Resumption of Activities – Avoid lifting heavy objects or engaging in intense physical activity for a few weeks.
Complications of Untreated Appendicitis
Ignoring appendicitis can lead to severe complications, including:
- Ruptured Appendix – If untreated, the appendix may burst, spreading infection throughout the abdomen (peritonitis).
- Abscess Formation – A pocket of pus may form around the appendix, requiring drainage before surgery.
- Sepsis – A life-threatening condition where infection spreads throughout the body.
Preventing Appendicitis
While there is no surefire way to prevent appendicitis, the following lifestyle changes may reduce the risk:
- Eat a High-Fiber Diet – Foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes promote a healthy digestive system.
- Stay Hydrated – Drinking plenty of water helps maintain smooth digestion.
- Avoid Processed Foods – Highly processed foods may contribute to digestive blockages.
- Regular Check-ups – If you have digestive issues, consult a doctor for early intervention.
When to Seek Medical Help
If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, especially severe abdominal pain, do not ignore it. Seek immediate medical attention to avoid complications.
Conclusion
Appendicitis is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and ensure a smooth recovery. If you or a loved one experiences symptoms of appendicitis, visit a healthcare professional immediately.
At Chetna Multispeciality Hospital, our expert surgeons provide advanced and safe treatments for appendicitis. Don’t ignore the pain—get treated today!
For Consultation Contact us on 8390861787 / 9158681123
Website – www.chetnahospital.co.in
Address – Chetna Hospital,
Sambhajinagar, MIDC, G Block, Near Rotary Club, Chinchwad 411019
#pune#pcmc#chinchwad#hospital#appendix#appendicitis#appendicitissymptoms#appendixpain#surgery#appendectomy#signsofappendicitis#acuteappendicitis#appendicitiscauses#appendixsurgery#appendicitistreatment#appendicitissurgery#appendicitispain#repturedappendix#appendixremoval#abdominalpain#surgicaldisease#acuteappendicitis#generalsurgeon