Comedones—commonly known as blackheads and whiteheads—are among the most frequent skin concerns faced by people of all ages. While they might seem like a minor issue, they can be stubborn, lead to acne breakouts, and affect skin texture and appearance. Understanding what comedones are, why they occur, and how to treat them safely can help you achieve clearer, healthier skin.
What Are Comedones?
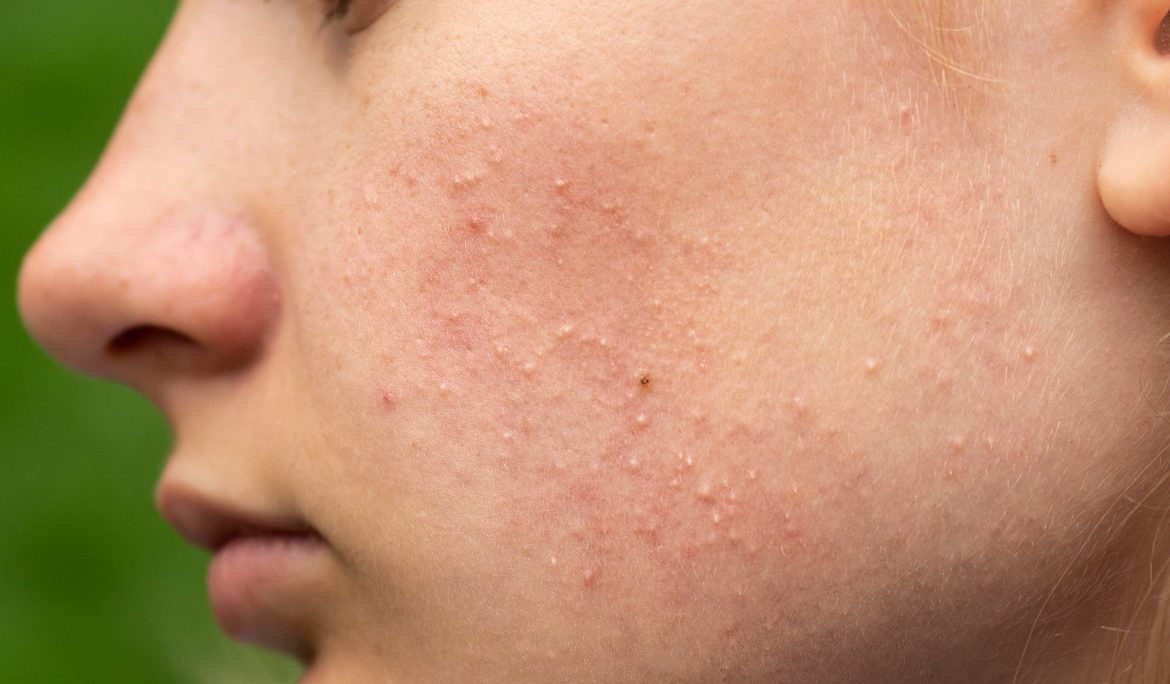
Comedones are small bumps that form on the skin when hair follicles become clogged with oil (sebum), dead skin cells, and sometimes bacteria. They are considered a type of acne lesion, but unlike inflamed pimples, comedones are usually non-inflammatory—though they can progress into red, painful acne if not treated properly.
The term “comedo” is singular, while “comedones” is plural. They are most commonly found on the face, particularly on the nose, chin, and forehead, but can also appear on the back, chest, and shoulders.
Types of Comedones
There are two main types of comedones:
1. Open Comedones (Blackheads)
- These occur when a clogged pore remains open at the skin’s surface.
- The trapped sebum and dead skin cells oxidize when exposed to air, turning dark in color—hence the name “blackhead.”
- Blackheads are not caused by dirt, although they may appear dirty due to the dark oxidation.
2. Closed Comedones (Whiteheads)
- These happen when the clogged pore remains closed, forming a small, flesh-colored or white bump under the skin.
- Since the pore is sealed, oxidation does not occur, so the contents remain light in color.
- Whiteheads can sometimes become inflamed and turn into pimples if bacteria grow inside.
What Causes Comedones?
Several factors contribute to the formation of comedones:
1. Excess Sebum Production
Oily skin is more prone to clogged pores due to overactive sebaceous glands.
2. Dead Skin Cell Build-Up
If skin cells are not shed properly, they can accumulate and block hair follicles.
3. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations—especially during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, or due to certain medications—can increase oil production.
4. Use of Comedogenic Products
Heavy creams, oils, or makeup products can block pores, leading to comedones.
5. Poor Cleansing Habits
Not removing makeup, sunscreen, and daily impurities can increase the risk of clogged pores.
6. Diet & Lifestyle Factors
High-glycemic foods, dairy products, stress, and lack of sleep can worsen skin congestion.
7. Environmental Factors
Pollution, humidity, and sweat can contribute to pore blockage.
Why You Should Not Squeeze Comedones at Home
While it might be tempting to squeeze a blackhead or whitehead, doing so can be harmful:
- Infection risk: Pushing bacteria deeper into the skin.
- Skin damage: Causing inflammation, redness, or permanent scarring.
- Spread of acne: Increasing the chance of breakouts in surrounding areas.
Professional Dermatologist Treatments for Comedones
A dermatologist can provide safe, effective, and customized treatments based on your skin type and the severity of comedones.
1. Professional Comedone Extraction
Using sterile instruments, dermatologists gently remove blackheads and whiteheads without damaging the skin. This is safer than at-home extraction and prevents scarring.
2. Chemical Peels
Peels with salicylic acid, glycolic acid, or lactic acid exfoliate the skin, remove dead cells, and help keep pores clear.
3. Topical Treatments
Dermatologists may prescribe:
- Retinoids (adapalene, tretinoin) to speed up cell turnover.
- Salicylic acid to dissolve oil and debris in pores.
- Benzoyl peroxide to control acne-causing bacteria.
4. Microdermabrasion
A gentle exfoliation procedure that helps unclog pores and improve skin texture.
5. HydraFacial or Medical Facials
These involve deep cleansing, exfoliation, and extraction for a clear, refreshed look.
Home Care Tips to Prevent Comedones
Even with professional treatment, daily skincare is crucial for preventing new comedones.
1. Cleanse Twice Daily
Use a gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser to remove oil, dirt, and makeup.
2. Exfoliate Regularly
Incorporate chemical exfoliants like AHAs (glycolic acid) or BHAs (salicylic acid) 1–2 times a week.
3. Use Non-Comedogenic Products
Choose skincare and makeup labeled “oil-free” or “won’t clog pores.”
4. Moisturize Daily
Even oily skin needs hydration—opt for lightweight, water-based moisturizers.
5. Apply Sunscreen
Use a non-comedogenic sunscreen every morning to protect from UV damage.
6. Maintain a Healthy Diet
Limit sugary and processed foods; include antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables.
7. Avoid Touching Your Face
Hands carry bacteria and oils that can clog pores.
When to See a Dermatologist
Seek professional help if:
- Comedones are persistent despite a good skincare routine.
- You have frequent breakouts or painful acne.
- You notice scarring or skin texture changes.
A dermatologist can identify the underlying cause and recommend targeted treatment for long-lasting results.
For Consultation Contact us on 96077 53535 / 9158681123
Website – www.chetnahospital.co.in
Address – Chetna Hospital, Sambhajinagar, MIDC, G Block, Near Rotary Club, Chinchwad 411019
.
.
.
#hospital#pune#pcmc#chinchwad#health#healthcare#skin#dermatologist#skinspecialist#skinclinic#hairdermatologist#skindoctor#dermatologistappointment#skincareprofessional#derma#skindr