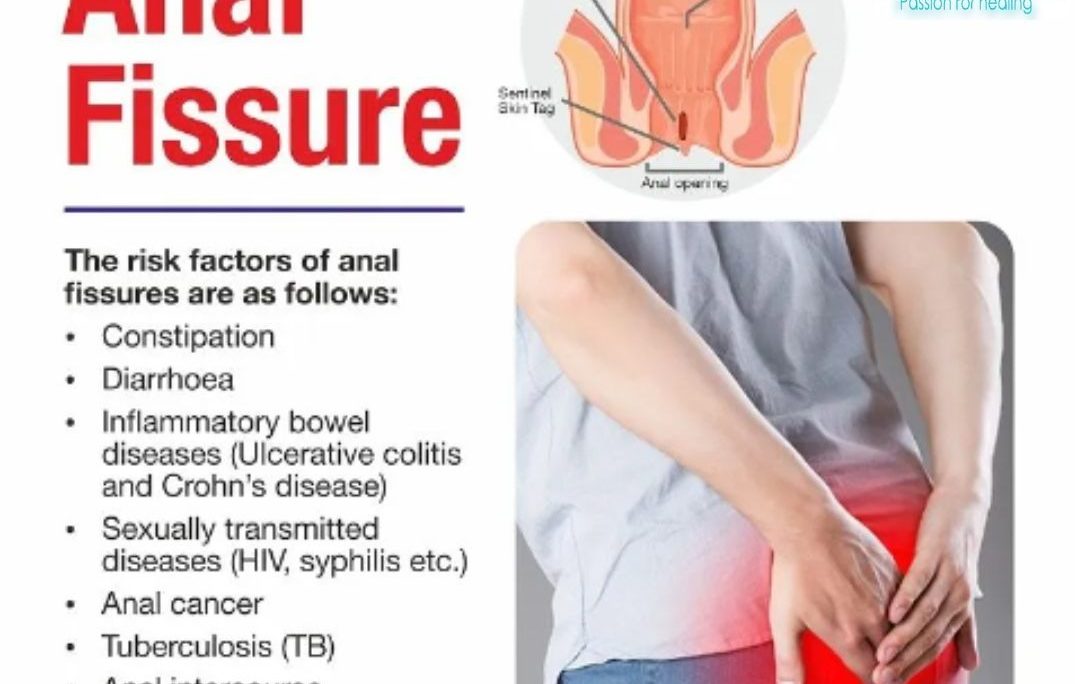
An anal fissure is a small tear in the lining of the anus, often leading to significant discomfort, especially during bowel movements. While it can affect anyone, certain factors make some individuals more susceptible than others. Understanding the risk factors can help in prevention and early treatment. In this blog, we’ll explore the various risk factors associated with anal fissures and what can be done to minimize the chances of developing them.
- Chronic Constipation
One of the most common risk factors for anal fissures is chronic constipation. When stool is hard and dry, it can cause strain during bowel movements. The pressure exerted while passing large or firm stools can tear the delicate lining of the anus. People with a low-fiber diet, inadequate water intake, or irregular bowel habits are more prone to constipation, making them at higher risk of developing fissures. - Chronic Diarrhea
While constipation is a well-known culprit, chronic diarrhea can also contribute to anal fissures. Frequent bowel movements or the passage of loose stools irritates the anal canal, making it more vulnerable to tearing. Recurrent diarrhea, often linked to gastrointestinal issues like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or infections, can weaken the tissue lining the anus, increasing the risk of fissures. - Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, which cause chronic inflammation in the digestive tract, significantly raise the risk of anal fissures. Crohn’s disease, in particular, can lead to inflammation and ulcers in the rectum and anus, making the tissue more susceptible to tears. Patients with IBD often experience both constipation and diarrhea, exacerbating the issue. - Childbirth
Pregnancy and childbirth are major risk factors for anal fissures in women. During labor, the intense strain and pressure on the pelvic region can cause the tissues in the anus to tear. Postpartum women, especially those who experienced vaginal delivery, often face constipation, which further increases the risk of developing fissures. - Anal Trauma
Trauma to the anal region, whether due to injury or medical procedures like surgery, can increase the likelihood of developing anal fissures. Even routine activities like anal intercourse can lead to trauma, especially if lubrication is insufficient or the tissue is already sensitive. Additionally, repeated straining during bowel movements can create microtears that develop into fissures over time. - Age
Both infants and older adults are more prone to anal fissures. Infants often develop fissures due to frequent bowel movements or passing hard stools. In older adults, reduced blood flow to the anal region, along with weakening of tissues, increases the risk. The reduced elasticity of skin and tissues in older individuals means they are more susceptible to tearing during bowel movements. - Tight or Overactive Anal Sphincter
Some people have a naturally tight or overactive anal sphincter, which makes them more vulnerable to fissures. The anal sphincter is a ring of muscle that helps control bowel movements. When it is excessively tight, passing stool becomes more difficult, increasing the chances of a tear. In some cases, the tension in this muscle can be due to stress or anxiety. - Previous Fissures
Having a history of anal fissures puts you at a higher risk of developing them again. Recurrent fissures are common, especially if the underlying causes, like constipation, diarrhea, or inflammation, are not addressed. Chronic fissures are also more difficult to treat and often require long-term management to prevent recurrence. - Sexual Practices
Certain sexual activities, particularly anal intercourse, may increase the risk of anal fissures. This happens due to the direct trauma to the anal region, especially if lubrication is not adequately used or if the tissues are sensitive. People who engage in such practices should take precautions, like using proper lubrication, to minimize the risk. - Medical Conditions
Underlying medical conditions like anal cancer, HIV, or other infections that compromise tissue integrity can increase the likelihood of anal fissures. These conditions can weaken the tissue in the anal region or lead to chronic inflammation, making it more prone to tearing.
For Consultation Contact us on 8390861787
Website – www.chetnahospital.in
Address – Chetna Hospital, Sambhajinagar, MIDC, G Block, Near Rotary Club, Chinchwad 411019